When it comes to home maintenance, understanding the components and systems of your bathtub can save you from unnecessary headaches and costly repairs. One of the most important things to learn in bathtub plumbing diagram is how to read a bathtub drain diagram.
In this ultimate guide, we will go over the anatomy of a bathtub drain, how to interpret a drain diagram, common issues and how to troubleshoot them, upgrading your drain system, and finally, a step-by-step guide to installing a new drain system.
Why understanding bathtub drain diagrams is important
Knowing how to read a bathtub drain diagram can help you identify potential issues before they turn into major problems. It also allows you to troubleshoot and fix any problems that arise more effectively. Additionally, if you decide to upgrade your bathtub drain plumbing, understanding the components and how they work together can help you choose the right bathtub plumbing system for your needs. By familiarizing yourself with a shower drain diagram, you can pinpoint any clogs or leaks in the system, determine the best course of action for repair or replacement, and ensure the proper functioning of your shower.
A brief overview of the bathtub drain diagram
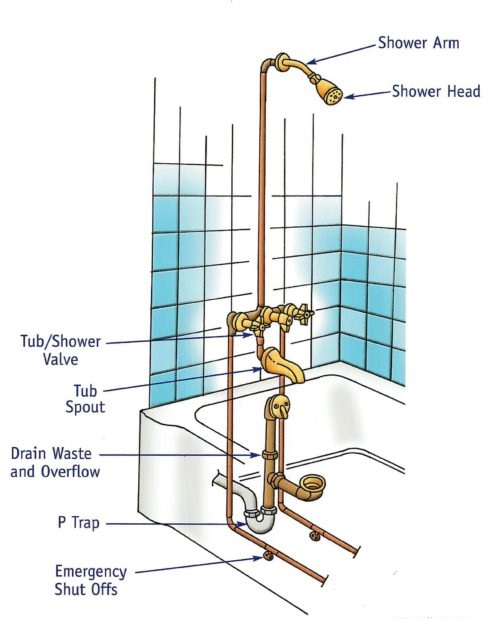
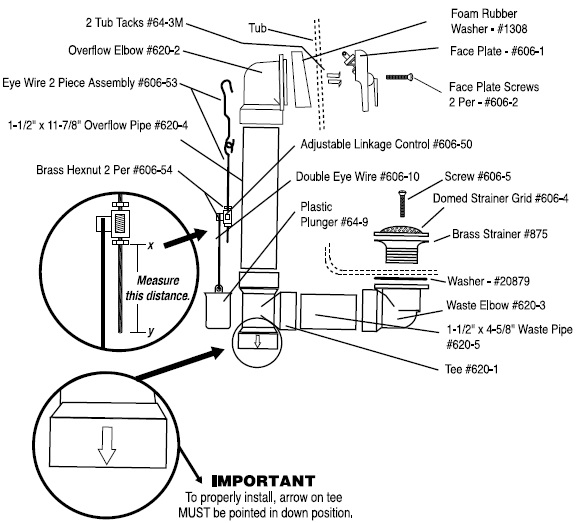
A bathtub drain diagram is a visual representation of the components and systems that make up your bathtub’s drainage system. It shows the location of the drain, overflow, and waste and overflow assembly, as well as the dimensions and measurements of each component.
Before diving into the details of the tub plumbing diagram, it’s important to understand some of the common terms and symbols used. For example, the drain itself is often represented by a circle with a vertical line through it, while the overflow is usually represented by a circle with a diagonal line through it. The assembly is often represented by a horizontal line with two circles on either end.
Anatomy of a Bathtub Drain
Different types of bathtubs and their drain systems
There are several different types of bathtubs, each with its own unique drain system. Some of the most common types include alcove, freestanding, drop-in, and corner tubs. Alcove tubs are typically installed against three walls and have a built-in apron, while freestanding tubs can be placed anywhere in the bathroom. Drop-in tubs are installed into a platform or surround, and corner tubs are designed to fit into a corner of the bathroom.
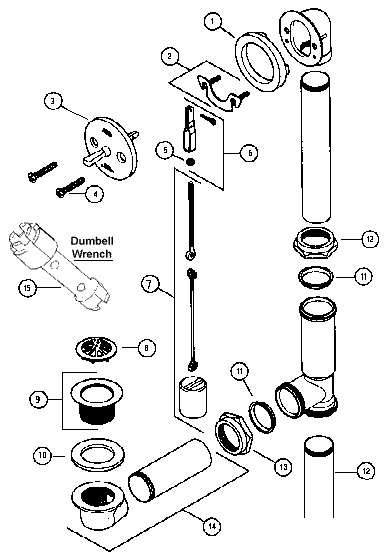
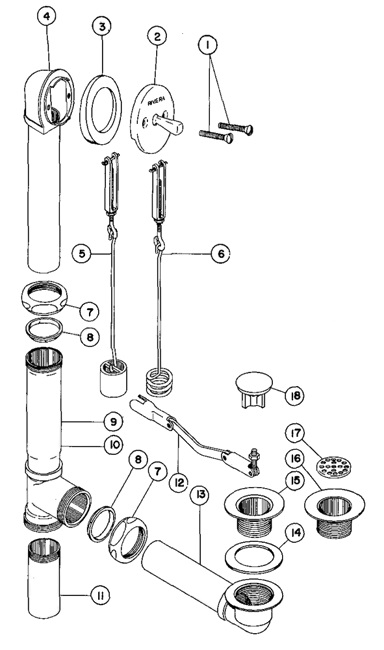
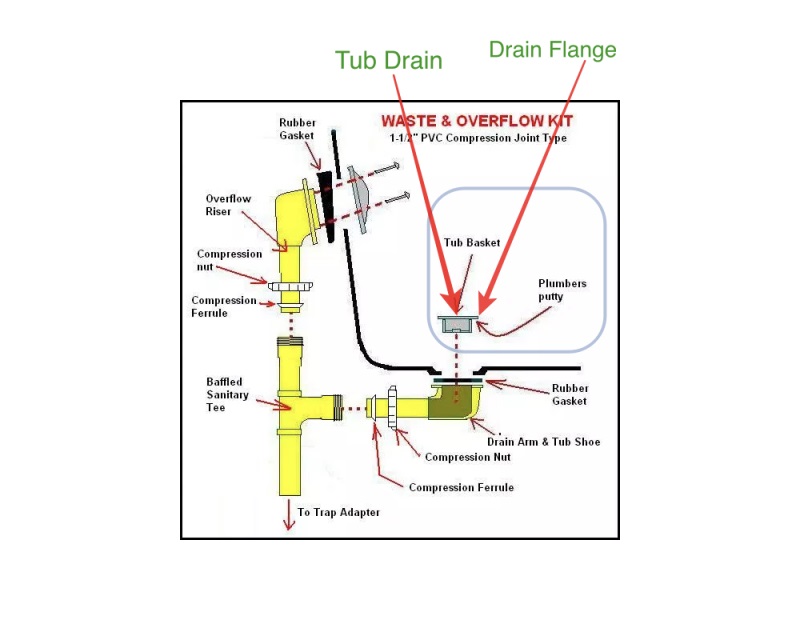
Components of a bathtub drain: overflow, waste and overflow assembly, drain shoe, and drain flange
Regardless of the type of bathtub you have, the components of the drain system are generally the same. The overflow is a hole located near the top of the bathtub that prevents water from overflowing onto the bathroom floor. The waste and overflow assembly is a system of pipes that controls the flow of water out of the bathtub. The drain shoe connects the assembly to the drain, and the drain flange is the visible part of the drain that is installed in the bathtub.
How the components work together to control water flow
The waste and overflow assembly is responsible for controlling the flow of water out of the bathtub. When you pull the lever on the overflow, it opens a valve that allows water to flow out of the tub and into the assembly. From there, the water flows through the drain shoe and into the drain, which leads to the bathtub plumbing system.
How to Interpret a Bathtub Drain Diagram
As mentioned earlier, the symbols used in a drain diagram can vary, but they generally follow a similar pattern. By familiarizing yourself with the symbols, you can quickly identify the location of the drain, overflow, and overflow assembly on the diagram.
Identifying the location of the drain, overflow
Once you understand the symbols used, identifying the location of each component on the diagram is relatively straightforward. The drain is typically located at the bottom of the diagram, while the overflow is near the top. The waste assembly is usually represented by a horizontal line connecting the drain and overflow symbols.
Reading the dimensions and measurements on the diagram
In addition to identifying the location of each component, a drain diagram also provides important dimensions and measurements. This includes the size of the drain flange, the distance between the drain and overflow, and the length of the assembly. Understanding these measurements can help you choose the right replacement parts if needed. In addition to identifying the location of each component, such as the drain and overflow, a shower drain diagram can also provide important details.
Troubleshooting Bathtub Drain Issues
There are several common issues that can occur with a bathtub drain, including clogs, leaks, and slow draining. Clogs are typically caused by a buildup of hair, soap scum, and other debris in the drain pipe. Leaks can be caused by a damaged waste and overflow assembly or a faulty drain flange. Slow draining is often caused by a clogged drain, but can also be the result of a damaged or poorly installed assembly.
Steps to take before attempting to fix a bathtub drain problem
Before attempting to fix a bathtub drain plumbing problem, it’s important to first assess the situation. For clogs, try using a plunger or drain snake to remove the blockage. If that doesn’t work, you may need to remove the drain flange and manually clear out the pipe. For leaks, check the waste and overflow assembly and drain flange for damage. Slow draining may simply require a thorough cleaning of the drain and waste and overflow assembly.
How to fix a clogged drain, leaky drain, and other common problems
Fixing a clogged drain may require the use of a plunger or drain snake, or removing the drain flange and manually clearing out the blockage. A leaky drain may require the replacement of the waste and overflow assembly or drain flange. Slow draining can often be fixed by cleaning the drain and waste and overflow assembly.
Upgrading Your Bathtub Drain System
Upgrading your bathtub drain plumbing can provide several benefits, including improved water flow and drainage, reduced risk of leaks and clogs, and increased durability and longevity of the system. Additionally, upgrading to a more efficient drain system can help you save water and reduce your water bill.
Types of bathtub drain systems available
There are several types of bathtub drain systems available, including traditional waste and overflow assemblies, cable-driven assemblies, and pop-up drain systems. Each has its own unique advantages and disadvantages, and the right choice will depend on your individual needs and preferences.
How to choose the right drain system for your Bathtub
When choosing a new drain system for your bathtub, consider factors such as the type of bathtub you have, your budget, and your personal preferences. Additionally, look for a system that is easy to install and maintain, and that provides reliable and efficient water flow and drainage.
DIY Bathtub Drain Installation
To install a new bathtub drain system according to the tub plumbing diagram, you will need several tools and materials, including a drain wrench, plumber’s putty, silicone caulk, and a new waste and overflow assembly or drain system. It’s important to have all of the necessary tools and materials before beginning the installation process.
The installation process will vary depending on the type of drain system you choose but generally involves removing the old drain system, preparing the bathtub for installation, and installing the new system. It’s important to follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully to ensure a successful installation.
Tips for ensuring a successful installation
To ensure a successful installation, be sure to thoroughly clean the bathtub and surrounding area before beginning. Additionally, carefully follow the manufacturer’s instructions and take your time to ensure that each component is installed correctly. Test the new drain system thoroughly before using the bathtub to ensure that everything is working properly. You can refer to a shower drain diagram provided by the manufacturer to get a clear understanding of the components and their installation process.
Conclusion
Understanding how to read a bathtub drain diagram is an important skill for any homeowner. By familiarizing yourself with the anatomy of
- bathtub drain plumbing
- interpreting drain diagrams
- troubleshooting common issues
- upgrading your drain system
- and even installing a new system yourself
You can save yourself time and money on repairs and maintenance. Remember to always follow the manufacturer’s instructions carefully and take the necessary precautions to ensure a safe and successful installation. By following the tips and guidelines outlined in this ultimate guide, you can maintain a reliable and efficient bathtub drain system for years to come.
Note: Explanation of the different parts of a typical bathtub drain
- Bathtub Drain Stopper: This is the part that you use to open and close the drain. It can be a plug, a lift-and-turn mechanism, a push-pull device, or a toe-touch style stopper.
- Strainer: Also known as a drain basket or drain cover, it’s the visible part of the drain that prevents larger objects like hair or debris from going down the drain.
- Overflow Plate: This is a cover with a small hole near the top of the bathtub. It helps prevent overflowing by allowing excess water to drain out if the water level gets too high.
- Overflow Pipe: Connected to the overflow plate, this pipe allows excess water to flow down into the main drainpipe.
- Drain Shoe: It’s a curved pipe that connects the bathtub drain to the main drainpipe. It often contains a gasket or seal to prevent leaks.
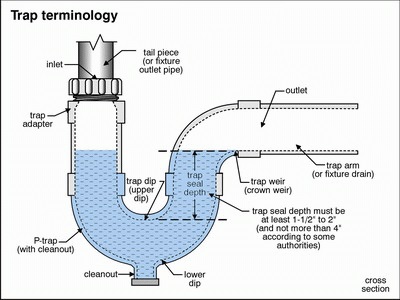
- Trap Assembly: This U-shaped pipe underneath the drain prevents sewer gases from entering your bathroom. It also catches debris, which can be removed for cleaning.
- Tailpiece: The straight pipe that connects the drain shoe to the trap assembly.
Understanding these parts can be helpful for basic maintenance or if you ever need to troubleshoot a bathtub drainage issue.
Frequently questions and answers for bathtub drain diagram
Q: What is the purpose of the overflow plate in a bathtub drain diagram?
A: The overflow plate helps prevent overflowing by providing an additional outlet for water if the water level in the tub gets too high. It connects to the overflow pipe, which channels excess water into the main drain.
Q: What is the function of the strainer in a bathtub drain?
A: The strainer, also known as a drain cover or basket, prevents larger objects like hair, debris, or jewelry from entering the drainpipe and causing clogs.
Q: How does the trap assembly in a bathtub drain work?
A: The trap assembly, typically a U-shaped pipe, serves multiple purposes. It prevents sewer gases from coming up through the drain and into the bathroom. Additionally, it catches debris and sediment, which can be removed for cleaning to maintain proper drainage.
Q: Why is the drain stopper important in a bathtub drain system?
A: The drain stopper controls the flow of water down the drain. It can be opened or closed to allow water to fill the tub or to release water when draining. It helps maintain water levels and prevents water from continuously draining while you’re using the tub.
Q: What’s the role of the tailpiece in a bathtub drain setup?
A: The tailpiece is a straight pipe that connects the drain shoe (the part under the tub) to the trap assembly. It provides a direct path for water to flow from the bathtub drain into the trap.
Understanding these components and their functions can assist in troubleshooting common bathtub drainage issues and performing basic maintenance to keep the drain system working effectively.